RO4: Detetcing and Preventing Cyberattacks via Malicious Browser Extensions

Web browser permissions policies and the lack of robust static and dynamic detection systems make malicious browser extensions a common tool for phishing, spying, fraud, and other advanced attacks. This work examines a range of attacks that can be executed using malicious extensions on Google Chrome and highlights the research gaps in existing prevention and detection measures. Through the analysis, we identify an initial set of malicious signatures associated with cyber fraud and spying, which are then used to develop a lightweight detection system that alerts users to potentially harmful extensions installed on their Chrome browser. Our system outperforms existing tools like Chrome Cleanup and Chrome Safeguard. Additionally, we introduce a new phishing technique that leverages malicious extensions, demonstrating its effectiveness through experiments on Chrome. This study aims to inform researchers and browser developers about the risks posed by such attacks and to encourage further research on detection and mitigation strategies.
Publications:
G. Varshney, M. Misra and P. K. Atrey. Cyberattacks via Google Chrome browser extensions. In World Scientific Reference on Innovation Volume 4: Innovation in Information Security, Eds. S. Goel, Y. Hong, J. Giboney and P. K. Atrey (Chapter 9), World Scientific Press, pp 193-210, (2018).[pdf][bibtex]
G. Varshney, M. Misra and P. K. Atrey. Detecting spying and fraud browser extensions. The 1st ACM International Workshop on Multimedia Privacy and Security (MPS'2017) in conjunction with the 24th ACM Conference on Computer and Communication Security (CCS'2017), Dallas, TX, USA, October 2017.[pdf][bibtex]
G. Varshney, M. Mishra and P. K. Atrey. Browshing: A new way of phishing using a malicious browser extension. IEEE Int. Conf. on Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT'2017), Vellore, India, April 2017. [Received: Best Paper Award] [pdf][bibtex]
RO3: LPD: A Lightweight Phish Detector
Web phishing is a common cyber-attack used to deceive internet users into revealing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, and social security numbers. While several phishing detection solutions exist, such as blacklists, search engines, heuristics, machine learning, visual similarity techniques, DNS, and proactive URL detection, many are resource-intensive and rely on third-party servers. Search engine-based approaches are among the most lightweight. This work introduces the Lightweight Phish Detector (LPD), a client-side phishing detection system for the Google Chrome browser.
Publications:
G. Varshney, M. Mishra and P. K. Atrey. A phish detector using lightweight search features. Elsevier Computers & Security Journal, Vol. 62, pp 213-228 (2016).[pdf][bibtex]
G. Varshney, M. Mishra and P. K. Atrey. Improving the accuracy of search engine based anti-phishing solutions using lightweight features. The 11th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions, Barcelona, Spain, December 2016.[pdf][bibtex]
RO2: Secure Authentication to Block RT MITM, CR MITM, and Malicious Extension Phishing Attacks
-
Securing user credentials against phishing is a challenging issue, especially with modern real-time (RT) and control relay (CR) man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and malicious browser extensions. Current authentication methods either fail to address these threats effectively, are complex, or require extra hardware like security keys. This work proposes a new anti-phishing authentication scheme using the Bluetooth address of the user's smartphone, app instance IDs, and a user password. Experimental results demonstrate that the scheme is secure against RT MITM, CR MITM, and malicious extension attacks while being efficient in memory and CPU usage. It also offers better usability and deployability compared to other equally secure methods.
Publications:
G. Varshney, M. Misra and P. K. Atrey. Secure authentication scheme to thwart RT MITM, CR MITM and malicious browser extension based phishing attacks. Elsevier Journal of Information Security and Applications, Vol. 42, pp 1-17 (2018).[pdf][bibtex]
G. Varshney, M. Misra and P. K. Atrey. A new secure authentication scheme for web login using BLE smart devices. The 11th IEEE International Conference on Anti-counterfeiting, Security, and Identification (ASID'2017), Xiamen, China, October 2017.[pdf][bibtex]
RQ1: Volatile Memory Forensics for Phishing Detection
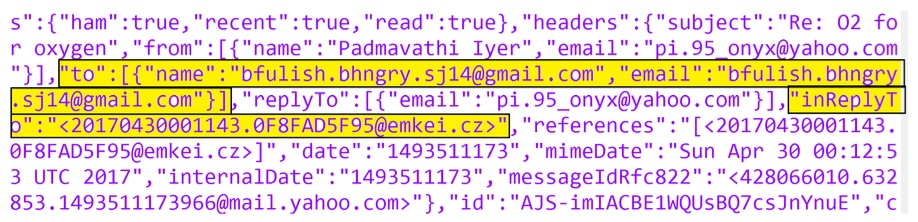
The internet is set to see an increase in DNS over HTTPS (DoH) traffic to enhance user privacy, making traditional DNS monitoring/filtering methods ineffective. This work proposes a novel approach to uncover DoH traffic by sniffing URLs directly from the RAM of endpoint devices, enabling organizations to monitor and filter content viewed on their systems, even when DoH is used to hide DNS queries. Additionally, we utilize memory forensics to detect email spoofing attacks by analyzing memory dumps to identify spoofed emails and whether clients replied to them. This approach provides non-repudiation, as all email interactions are stored in the system's physical memory, allowing investigators to trace and verify email spoofing incidents effectively. Experimental results demonstrate the feasibility, effectiveness, and robustness of our method for both DoH traffic analysis and email spoofing detection.
Publications:
G. Varshney, P. Iyer, M. Misra and P. K. Atrey. Evading DoH via live memory forensics for phishing detection and content filtering. The 13th International Conference on COMmunication Systems & NETworkS (COMSNETS'2021) - Blockchain Workshop, Bengaluru, India, January 2021.[pdf][bibtex]
P. Iyer, P. K. Atrey, G. Varshney and M. Mishra. Email spoofing detection using volatile memory forensics. The 3rd IEEE Network and Cloud Forensics Workshop (NFW 2017) in conjunction with IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS 2017), Las Vegas, NV, USA, October 2017.[pdf][bibtex]
 Pradeep Atrey's Research on
Pradeep Atrey's Research on 


